
93) “hookingĪnd unhooking that last phosphate is what keeps the whole Recycled in the mitochondria where it is recharged and comes outĪgain as ATP. That removes one of the phosphate-oxygen groups, leaving adenosineĭiphosphate (ADP). Liberated from the ATP molecule to do work in the cell by a reaction Where ATP manufacture occurs (Goodsell, 1996, p.74). Thisīinding blocks the electron transport system in the mitochondria Certain cyanide compounds, for example, are poisonousīecause they bind to the copper atom in cytochrome oxidase. A steady supply of ATP is so critical that a poison whichĪttacks any of the proteins used in ATP production kills the organism Nutrients contain energy in low-energyĬovalent bonds which are not very useful to do most of kinds ofīonds must be translated to high energy bonds, and this is a role The energy level it carries is just the right amountįor most biological reactions. The simplest bacteria to humans use ATP as their primary energyĬurrency. (See Figure 1 for a simple structural formula andĪ space filled model of ATP.) As far as known, all organisms from The nucleoside adenosine and a tail consisting of three 62).įor adenosine triphosphate, a complex molecule that contains To trade in its unique currency” (Kornberg, 1989, p.
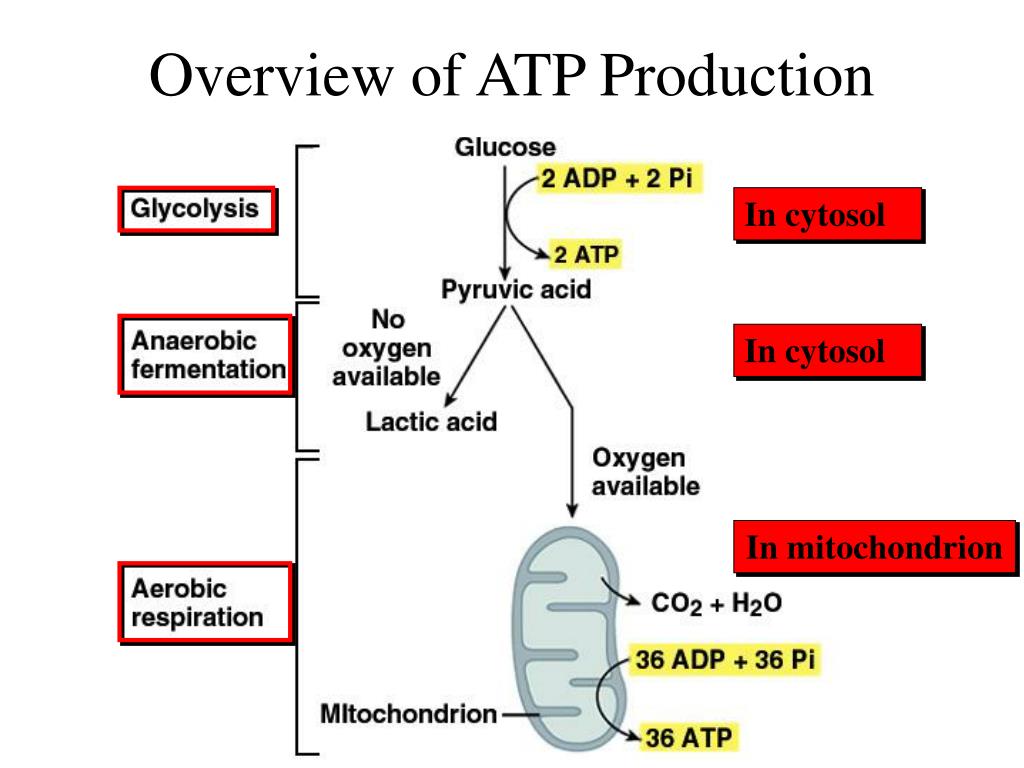
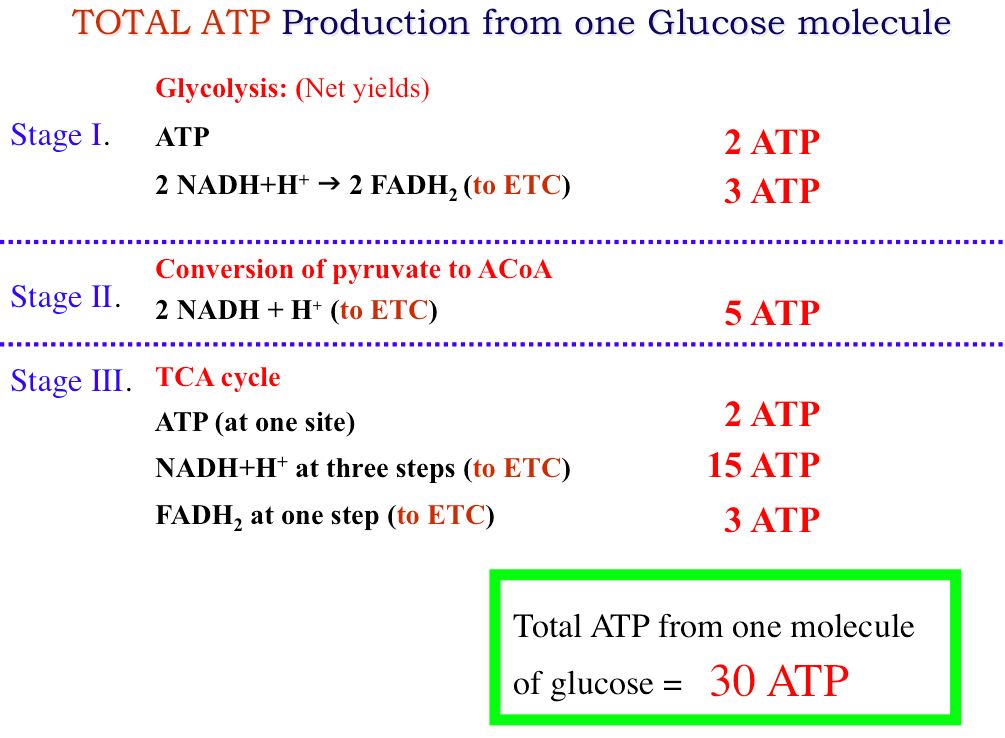
Imagine the metabolic confusion if this were not so: Each of theĭiverse foodstuffs would generate different energy currenciesĪnd each of the great variety of cellular functions would have Turn powers virtually every activity of the cell and organism. Nature, all foodstuffs of living things, produce ATP, which in Is “used to build complex molecules, contract muscles, generateĮlectricity in nerves, and light fireflies. The “most widely distributed high-energy compound within Machine that fits the standard definition of a machine. A nanomachine is a complex precision microscopic-sized That serves as the primary energy currency of the cell (Trefil,ġ992, p.93). Macromoleculearguably “second in importance only toĭNA”is ATP. Even below this levelĪre other parts so small that they are formally classified asįig. Cell organelles include mitochondria, GolgiĬomplexes, microtubules, and centrioles. Which in turn are constructed from yet smaller machines knownĪs organelles. TheseĬomplex life units are made from still smaller parts called cells Examples include unitsĬalled organs such as the liver, kidney, and heart. Necessary in its entirety in order for even the simplest formĮvery machine requires specific parts such as screws, springs,Ĭams, gears, and pulleys. This motor isĪn excellent example of irreducible complexity because it is Of enormously intricate nanomachines that needs to have beenĭesigned in order for life to exist on earth. This complex molecule is critical for all lifeįrom the simplest to the most complex. 1 of the Creation Research Society Quarterly,Ĭurrency molecule of the cell, ATP, is evaluated in the context During this conversion 2 ATP molecules are generated in the 7 t h F A D H 2 through the Krebs cycle.© 1999 by Creation Research Society. During the second stage, the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate formed is broken down into 2 molecules of pyruvate. This conversion occurs in 5 steps that are mediated by the utilization of 2 ATP molecules. Stage 1 is regarded as the Preparatory stage where the glucose molecule converts 2 molecules of Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. The complete glycolysis is divided into two stages comprising of 5 steps in each stage. Apart from ATP, NADH is also released that are subjected to oxidation through the electron transport chain resulting in the production of ATP mediated by an enzyme ATP synthase. This SLP is under the control of Phosphoglycerate kinase and pyruvate kinase. It gives rise to 2 ATP using substrate-level phosphorylation. Glycolysis is the process of metabolizing glucose and glycerol into pyruvate. Where glycolysis and beta oxidation gives 30 ATP molecules for a single glucose molecule Three major metabolic processes involved in the production of ATP are as follows: 1) Glycolysis 2) Beta oxidation 3) TCA cycle or Oxidative phosphorylation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
